How Technology Solves Common Analyst Challenges: Integration, Data Silos, and Risk Management
Introduction: The Evolving Analyst Landscape
Analysts play a crucial role in today’s organizations, driving insights and strategic decisions. Yet, they frequently encounter significant challenges that hinder efficiency, accuracy, and impact. Technology is often applied as a solution, but which challenges does it really solve, and how can organizations leverage modern tools to empower their analysts? This article explores the most common obstacles-like integration challenges, data silos, and risk management-and provides actionable guidance for implementing technology-driven solutions.
1. Integration Challenges: Aligning Disparate Systems
One of the most persistent analyst obstacles is system integration . Many organizations use a patchwork of software, databases, and legacy systems, which can be difficult to connect. When systems do not communicate seamlessly, analysts face delays, incomplete data, and inaccurate reporting. Integration issues may also arise during mergers, acquisitions, or digital transformation initiatives.
To address this, organizations are increasingly turning to integration platforms and scalable architectures. By conducting a comprehensive assessment of the existing tech stack, analysts and IT leaders can identify incompatibilities and select technologies designed for interoperability. For example, using application programming interfaces (APIs) or middleware can bridge gaps between systems, allowing data to flow smoothly between departments.
In practice, businesses often collaborate with IT to evaluate potential solutions before implementation. Cloud-based integration services and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems are popular choices because they support real-time data exchange and flexibility. Early planning and cross-departmental alignment are critical for a successful rollout. According to industry experts, a thorough integration strategy not only improves efficiency but also enables better decision making by providing a holistic view of organizational data [1] .
Implementation Steps:
- Map all existing systems and data flows within the organization.
- Identify integration gaps and prioritize based on business impact.
- Evaluate integration platforms and select those compatible with current and future needs.
- Collaborate with IT for configuration, testing, and deployment.
- Train analysts and stakeholders on new workflows and capabilities.
Potential Challenges & Solutions: Resistance to change is common; clear communication and hands-on training can foster buy-in. Technical issues may require support from experienced vendors or consultants.
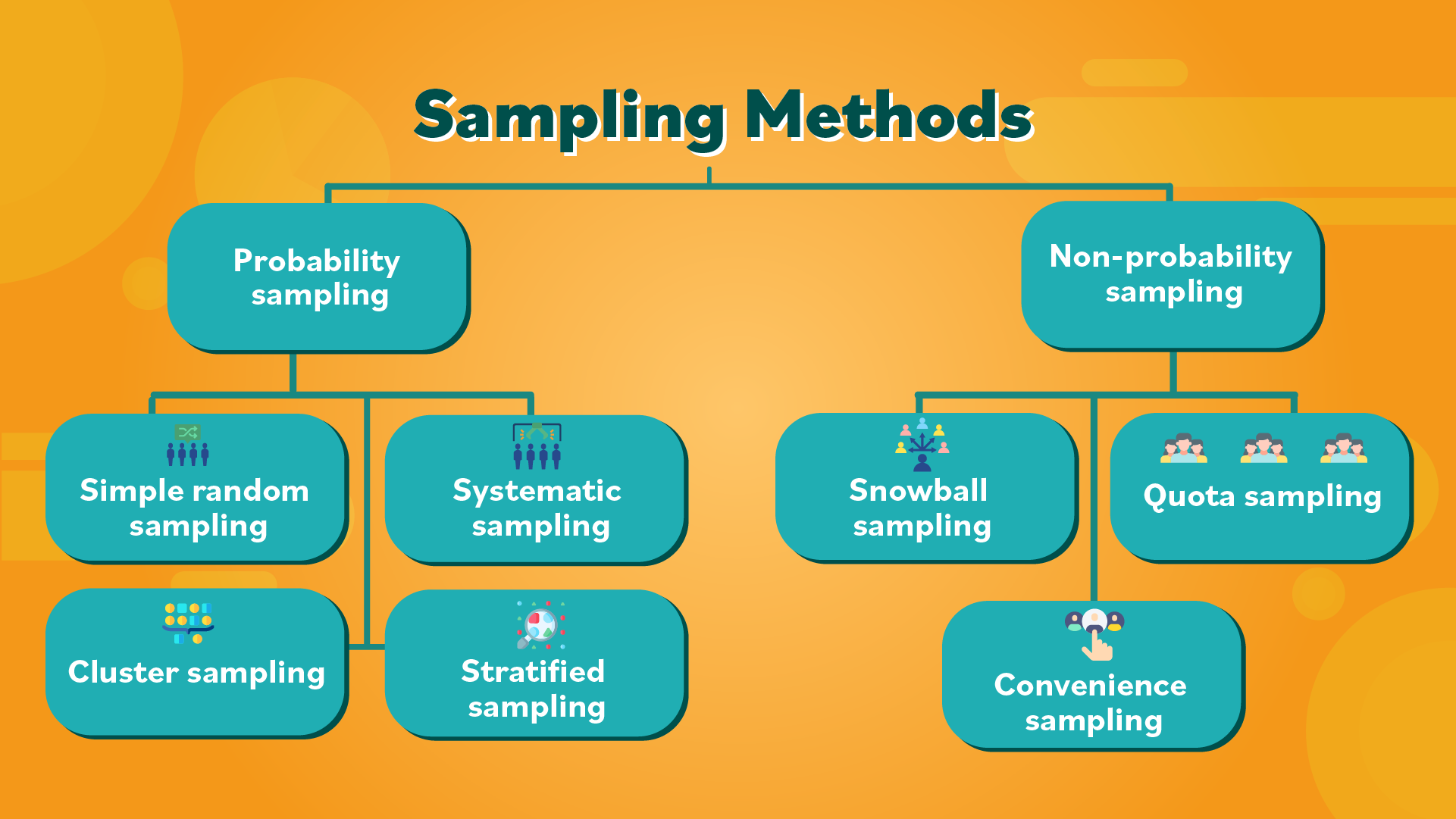
2. Data Silos and Access Issues
Another prevalent challenge is the presence of data silos . When different departments or branches store information in isolated systems, analysts struggle to access the complete picture. This fragmentation leads to inefficiencies, duplicated efforts, and potentially faulty insights.
Technology addresses this by enabling unified data platforms and cloud-based analytics solutions. For example, implementing a modern data warehouse allows information from various sources to be consolidated and standardized. This ensures that analysts have timely access to accurate, organization-wide data. A well-integrated business intelligence (BI) tool can further break down silos, empowering analysts to generate cross-functional reports [4] .
Organizations may also adopt data governance frameworks to maintain consistency, security, and accessibility. These frameworks clarify ownership, usage policies, and quality standards across the enterprise.
Implementation Steps:
- Conduct an audit to identify all data repositories and ownership structures.
- Develop a unified data strategy, focusing on centralization or seamless connectivity.
- Invest in cloud-based data warehouses or data lakes for scalable storage and access.
- Deploy BI tools that support self-service analytics across departments.
- Create data governance policies to maintain data integrity and compliance.
Real-World Example: One organization implemented a cloud data stack and a modern BI tool, resulting in real-time revenue reporting for executives and operational dashboards for product and engineering teams. This shift enabled faster, more informed decision making and improved collaboration [5] .
Alternative Approaches: For smaller organizations or those with limited budgets, phased integration of key data sources may be more feasible. Open-source tools and data connectors can also provide cost-effective solutions.
3. Slow Analytics and Reporting Bottlenecks
Many analysts face slow analytics due to outdated tools, manual processes, or overwhelming data volumes. Delays in generating reports can negatively impact business decisions, especially when timely insights are critical.
Technological solutions include automated data pipelines, cloud-based processing, and self-service BI platforms. By automating data collection, transformation, and visualization, analysts spend less time wrangling data and more time generating valuable insights.
Organizations can further optimize analytics by investing in ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) tools that streamline data movement and ensure rapid updates. Real-time dashboards provide up-to-the-minute visibility for stakeholders, reducing reliance on static spreadsheets and manual reporting cycles.
Implementation Steps:
- Assess current analytics workflows to identify bottlenecks.
- Automate repetitive tasks with data pipeline tools and scripting.
- Adopt cloud-based analytics solutions for scalable processing power.
- Empower non-technical users with self-service BI platforms.
- Continuously monitor performance and iterate on workflows for further improvements.
Case Study: A software company’s CFO transitioned from spreadsheet-based reporting to a real-time dashboard, enabling instant financial insights for decision makers. This shift improved responsiveness and data-driven strategy across departments [5] .
4. Risk Management and Regulatory Compliance
In a landscape of increasing complexity, risk management and regulatory compliance pose ongoing challenges for analysts. Rapid technological change, evolving regulations, and scrutiny from oversight bodies require constant vigilance and agile response.
Technology enables proactive risk detection, automated compliance monitoring, and efficient control management. Modern risk management platforms leverage analytics and artificial intelligence to identify, quantify, and mitigate potential threats. These systems help organizations keep pace with regulatory demands, maintain stakeholder trust, and improve transparency.
Implementation Steps:
- Identify key risk areas and compliance requirements relevant to your industry.
- Evaluate risk management platforms that offer automation, reporting, and real-time monitoring.
- Integrate risk systems with existing data sources for comprehensive oversight.
- Train staff on compliance processes and platform usage.
- Regularly review and update controls as regulations and business needs evolve.
Alternative Solutions: For organizations not ready for full automation, periodic risk assessments and manual monitoring can still provide value. However, as complexity grows, technology becomes increasingly important for scalability and accuracy [2] .
5. Overcoming Resistance to Change
Implementing new technologies often triggers resistance to change among stakeholders. Concerns about disruption, the learning curve, or perceived threats to job security can slow or derail technology adoption. Overcoming this resistance is vital for analysts seeking to drive innovation and improvement.

Source: fity.club
Successful organizations invest in comprehensive change management strategies. This includes transparent communication, demonstrating the tangible benefits of new tools, and involving employees in the implementation process. Ongoing training, user support, and feedback mechanisms help build confidence and ensure a smooth transition.
Practical Steps:
- Engage stakeholders early and clearly articulate the value of the proposed technology.
- Offer hands-on training sessions and accessible support resources.
- Encourage feedback and incorporate user suggestions into the rollout.
- Highlight early wins and success stories to build momentum.
- Maintain open communication channels for questions and concerns.
Key Takeaway: Technology adoption is as much about people as it is about systems. Empower analysts and stakeholders through involvement, education, and support to maximize ROI on technology investments [1] .
6. Step-by-Step Guidance for Accessing Solutions
If you’re seeking to apply technology to overcome analyst challenges in your organization, consider the following steps:

Source: wallpaperaccess.com
- Assess your current analyst workflows, identifying pain points such as integration, data silos, or slow reporting.
- Engage with IT and business stakeholders to prioritize challenges based on business impact.
- Research modern technology solutions, focusing on scalability, compatibility, and user adoption. Use reputable sources such as industry analyst reports and official vendor documentation.
- Request demonstrations or pilot programs from technology providers to evaluate fit.
- Develop a phased implementation plan, including training and change management strategies.
- Monitor progress, gather feedback, and iterate to continually refine your technology stack and analyst processes.
For guidance on selecting data analytics platforms or risk management tools, you can consult official vendor websites, industry analysts, or professional associations such as the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA) or KPMG’s risk management resources. If you are interested in vendor-neutral advice, consider searching for “business analyst technology integration best practices” or “data analytics implementation guidance” through well-known technology consultancies and research groups.
References
MORE FROM couponito.com