Exploring the Science: Can Sound Travel Through Space?
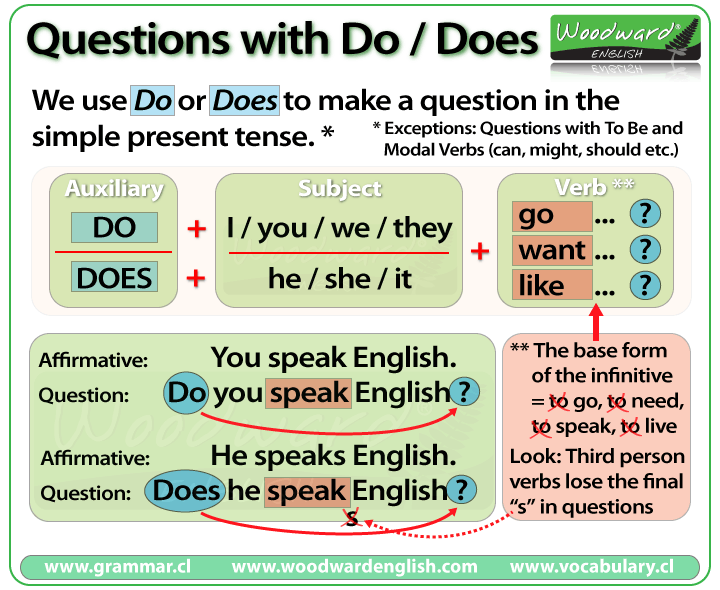
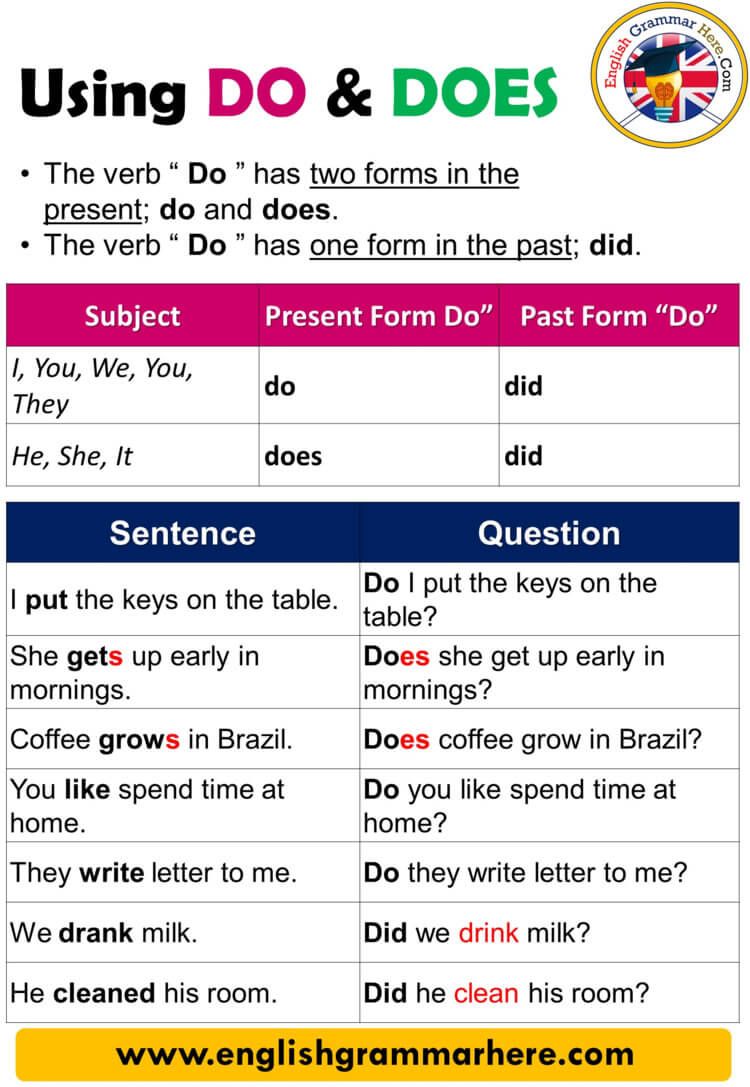
Understanding the Basics: How Sound Travels
Sound is a type of energy that moves as a mechanical wave , requiring a medium such as air, water, or solid material to travel. On Earth, sound waves are created when an object vibrates, causing nearby molecules to bump into each other and transmit the vibration outward. This chain reaction of energy transfer is what ultimately reaches our ears as audible sound. For example, when you speak, your vocal cords vibrate and compress the air, sending waves that your listener perceives as sound. This process is similar to pushing one end of a stretched Slinky toy-waves ripple from one end to the other through the coils, just as sound propagates through air molecules [2] .
The Nature of Space: Why Is It So Silent?
Space, generally speaking, is a vacuum . This means it is almost completely devoid of the particles-atoms and molecules-that are needed for sound waves to travel. On Earth, air provides a dense network of molecules that can easily transmit vibrations. In contrast, the vast emptiness of space lacks these particles, making it impossible for sound to propagate in the traditional sense. This is why famous phrases like “in space, no one can hear you scream” are scientifically accurate: there is no medium in most of space to carry the sound waves [3] [4] .
Recent Discoveries: Exceptions to the Rule
While the general rule is that sound cannot travel through the vacuum of space, recent scientific experiments have demonstrated limited exceptions under highly specialized conditions. In a groundbreaking 2023 study, researchers managed to transmit sound waves across a vacuum by using two zinc oxide crystals. These crystals are piezoelectric, meaning they can convert mechanical vibrations into electrical charges. When sound was applied to one crystal, it generated an electric field disruption, which could be picked up by the second crystal on the other side of a vacuum gap. This process is called “tunneling,” and while it technically sends sound information across a vacuum, it does not do so in a way that would be audible to the human ear or practical over long distances. The effect only works over microscopic distances and requires specific physical setups [1] .
Common Misconceptions and Sci-Fi Myths
Many popular movies and TV shows portray space battles with dramatic explosions and roaring engines. In reality, such sounds would be impossible to hear in the vacuum of space because there is no air or other medium to carry the sound waves. Astronauts working outside the International Space Station, for example, cannot communicate by shouting or making noise; they rely on radios that transmit their voices as electromagnetic waves, which do not require a medium and can travel through the vacuum of space [3] [2] [4] .

Source: dreamstime.com
Applications and Real-World Examples
On Earth, the principles of sound transmission are used in everything from music to medicine. For example, ultrasound technology relies on sound waves traveling through bodily tissues to create images of internal organs. In underwater communication, sound travels efficiently through water, allowing for sonar mapping and submarine communication. In contrast, space engineers and scientists must design technology that does not depend on mechanical waves. Communication in space is achieved with electromagnetic waves (like radio), which do not require a physical medium and can travel vast distances across the cosmos [2] .
How to Explore Sound and Space Further
For students, educators, or enthusiasts interested in learning more about the intersection of sound and space, there are several paths to explore:

Source: dreamstime.com
- Visit a Science Museum or Planetarium: Many institutions, such as the Adler Planetarium, offer exhibits and educational programs on space and physics. Check their official websites for event listings and resources. You can also follow their verified social media channels for live events and Q&A sessions [3] .
- Participate in Online Courses: Look for free or paid courses on physics and astronomy from reputable platforms like Coursera, edX, or Khan Academy. Search for keywords such as “physics of sound” or “introduction to astronomy.” These platforms are verified and provide high-quality, accessible learning content.
- Engage with Experts: Many universities and scientific organizations offer public lectures, webinars, and online Q&A forums. For example, you can submit questions to programs like “Ask Dr. Universe” from Washington State University, where scientists answer student questions about space and science [5] .
- Conduct Simple Experiments: To understand how sound travels, try experiments at home using different media. For instance, use a metal rod, a water-filled balloon, and a rubber band to observe how sound behaves in solids, liquids, and air. Document your observations and compare them to what you learn about the vacuum of space.
Challenges and Solutions in Sound Transmission Beyond Earth
The greatest challenge in transmitting sound through space is the absence of a medium. All traditional sound communication tools fail in the vacuum. To overcome this, spacecraft and astronaut suits are equipped with radios and electronic communication devices that transmit information using electromagnetic waves. For future space exploration, researchers are exploring quantum communication and advanced signaling technologies that do not depend on sound waves.
If you are interested in pursuing a career or education in this field, consider these steps:
- Study Physics and Engineering: High school and college courses in physics, mathematics, and engineering will provide a solid foundation. Explore programs accredited by recognized bodies such as ABET or the American Physical Society for verified quality.
- Join Astronomy Clubs or Competitions: Local and national organizations often host science fairs, astronomy nights, and engineering challenges. Look up your area’s official science education organizations for opportunities.
- Connect with Professional Societies: The American Astronomical Society and similar organizations offer resources, career guidance, and networking for aspiring scientists and engineers. Visit their official websites or contact them for more information.
Summary and Key Takeaways
In summary, sound cannot travel through the vacuum of space because there are not enough particles to transmit vibrations. While cutting-edge experiments have demonstrated the theoretical possibility of transmitting sound energy across a vacuum at microscopic scales, this does not change the reality that space remains silent for all practical purposes. If you are eager to learn more, connect with verified educational and scientific organizations, participate in their programs, and use trusted platforms for in-depth study.
References
- [1] Space.com (2023). Turns out you can transmit sound in a vacuum, just not very far.
- [2] Astronomy.com (2024). Is there any sound in space? An astronomer explains.
- [3] Adler Planetarium (2025). Can You Hear Sound In Space?
- [4] Caltech Cool Cosmos. Can you hear sound in space?
- [5] YouTube (2021). Can You Hear In Space? – Ask Dr. Universe.
MORE FROM couponito.com