Do You Need a Real Estate Agent or College to Buy or Sell a Home? Here’s What You Need to Know
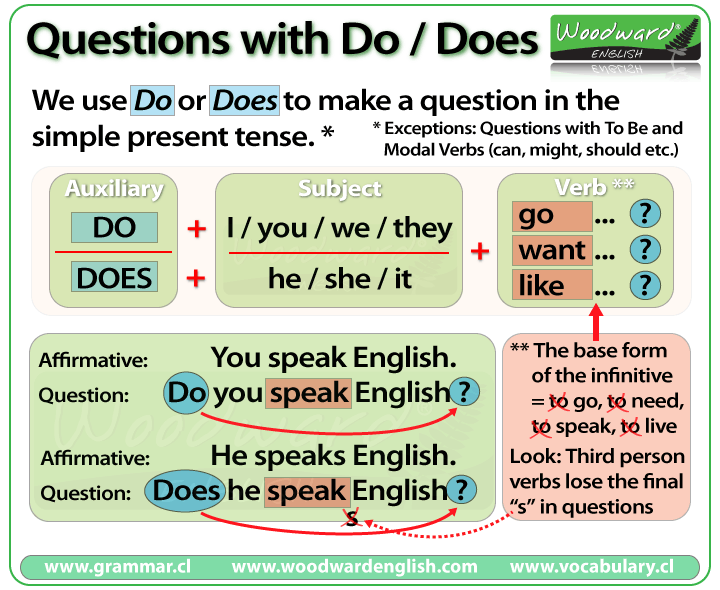
Understanding If You Need a Real Estate Agent to Buy a House
When considering buying a house, one of the first questions many potential homeowners ask is whether they need to work with a real estate agent . The short answer is: no, it is not legally required to have an agent represent you during a home purchase in the United States. However, many buyers choose to use an agent for several practical reasons.

Source: magiadedonetzka.blogspot.com
Real estate agents provide expertise in negotiations, paperwork, and market analysis, often streamlining the process for buyers who are unfamiliar with local markets and legal requirements. Agents can help you:
- Find properties that match your criteria
- Negotiate price and contract terms
- Guide you through inspections, appraisals, and closing procedures
For those who prefer to buy a home without an agent , you can directly contact sellers, attend open houses, and work with a real estate attorney to handle contracts and closing paperwork. Some buyers prefer this route for privacy or to avoid agent commissions. However, it’s important to be aware that you’ll need to take responsibility for:
- Researching local market conditions
- Handling negotiations and legal documents
- Coordinating inspections, appraisals, and closing logistics
If you decide to proceed without an agent, consider consulting a real estate attorney to ensure compliance with local laws and protect your interests. You can search for qualified attorneys through your state’s bar association or legal referral services.
Do You Need a College Degree for Real Estate Careers?
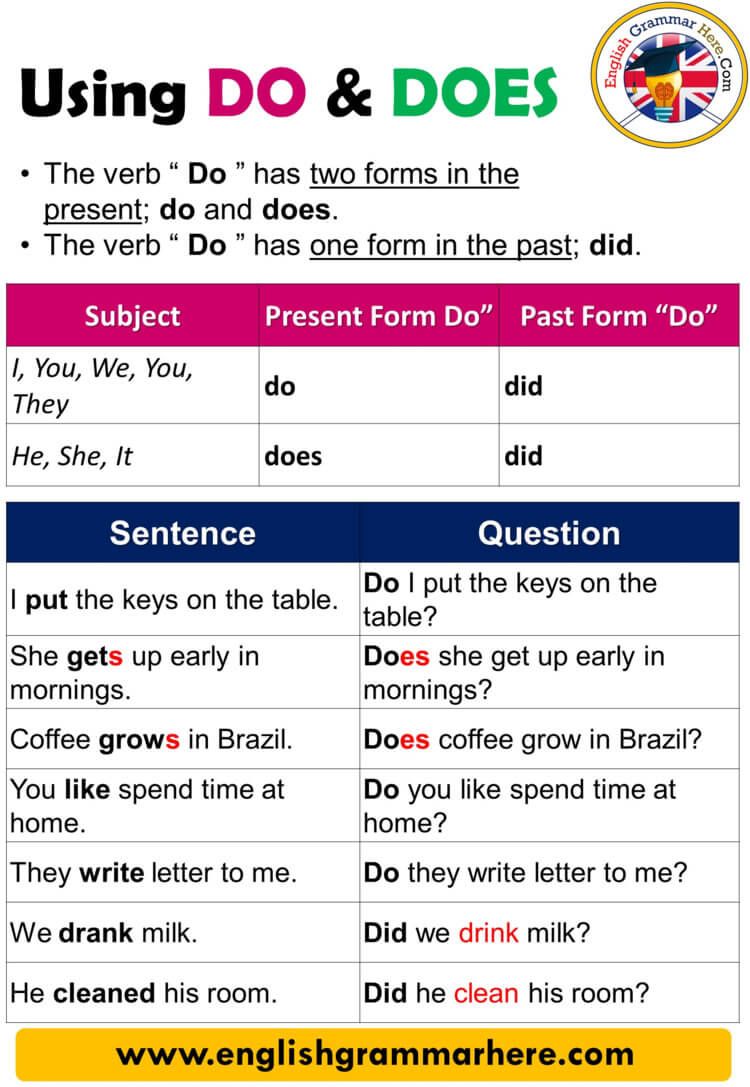
College education is not required to become a licensed real estate agent in the U.S. Instead, most states require candidates to:
- Be at least 18 or 19 years old
- Complete a specified number of hours of pre-license real estate education from an approved provider
- Pass a state licensing exam
- Submit to background checks and complete all licensing paperwork
For example, in Tennessee, prospective affiliate brokers must complete 60 hours of real estate education and provide proof of high school graduation, but a college degree is not required. After passing the licensing exam, additional training is required before a license is issued [1] . Massachusetts requires 40 hours of pre-licensing coursework for salespersons and a passing exam score. There is no mention of a college degree requirement, only that applicants be at least 18 years old and have a social security number [3] . Virginia requires a 60-hour “Principles of Real Estate” course and passing exam, with no college prerequisite [5] .
These requirements vary by state, so it’s important to check with your state’s real estate regulatory board or commission for the latest details. You can typically find these agencies by searching “[State] Real Estate Commission” or visiting your state’s official government website.
How to Become a Licensed Real Estate Agent: Step-by-Step Guide
Pursuing a career as a real estate agent can be accomplished without a college degree. Here’s a step-by-step overview of the licensing process:
- Meet Age and Residency Requirements: Most states require applicants to be at least 18 or 19 years old and have legal residency status [2] .
- Complete Pre-License Education: Enroll in an approved real estate education course (typically 40-60 hours depending on the state). You may find trusted providers through your state’s real estate commission, local community colleges, or major online education platforms.
- Pass the State Licensing Exam: After completing the education requirement, register for the licensing exam. Most states require a passing score to continue. Exam details and registration instructions are available on your state’s real estate licensing website.
- Background Check and Application: Submit fingerprints and complete a background check. Fill out the application form and submit proof of education, exam results, and any required fees.
- Obtain Errors and Omissions Insurance: Many states require proof of insurance before issuing a license.
- Find a Sponsoring Broker: New agents often need to work under a licensed broker. Research local brokerages and interview to find a good fit for your career goals.
Once licensed, you can pursue advanced certifications and designations through organizations such as the National Association of REALTORS® (NAR) [4] . These programs can help you specialize in areas like pricing strategy, negotiation, or resort properties and expand your professional network.

Source: jvferrandez.blogspot.com
Benefits and Drawbacks of Using a Real Estate Agent
Choosing whether to use a real estate agent involves weighing several benefits and drawbacks. Here are some considerations:
Benefits:
- Market Expertise: Agents know local market trends, helping you make informed decisions.
- Negotiation Skill: Experienced agents negotiate on your behalf for the best price and terms.
- Legal Protection: Agents help ensure all paperwork is completed correctly and comply with regulations.
- Access to Listings: Agents have access to MLS databases and can quickly find suitable properties.
Drawbacks:
- Cost: In most cases, the seller pays the agent commission, but buyers may encounter agent fees in some situations.
- Less Control: Working with an agent means sharing decision-making and negotiation authority.
For buyers who want full control or wish to avoid commission costs, buying without an agent is possible but requires careful preparation and professional legal help.
Alternative Pathways and Resources
If you’re considering a real estate career but do not meet the traditional requirements or want additional flexibility, there are alternative pathways and resources available:
- Online Education: Many approved providers offer online pre-license courses, which can be completed at your own pace. Search for “real estate pre-license course online [Your State]” for options.
- Community Colleges: Some offer real estate courses or certificate programs that fulfill licensing requirements.
- Professional Associations: The National Association of REALTORS®, your state’s real estate commission, and local boards offer professional development, networking, and support.
- Mentorship and Internships: Connect with experienced agents or brokers for guidance and hands-on learning. Local brokerages often offer mentorship programs.
If you’re unsure how to begin, contact your state’s real estate commission directly or search for “How to become a real estate agent in [Your State]” on trusted education provider sites.
Key Takeaways and Next Steps
To recap, you do not need a real estate agent to buy a house, but working with one provides valuable expertise, protection, and convenience. College education is not required to become a real estate agent. Instead, focus on completing your state’s pre-license education, passing the exam, and fulfilling all application requirements.
If you’re ready to begin a real estate career:
- Check your state’s official real estate commission website for specific licensing requirements
- Research approved education providers and enroll in pre-license courses
- Prepare for the licensing exam with practice resources
- Find a reputable broker to sponsor you as you start your career
For homebuyers, decide whether you want to use an agent based on your comfort with negotiations, legal paperwork, and market knowledge. Consider consulting a real estate attorney if you choose to buy without an agent.
With the right resources and planning, you can successfully navigate buying a home or launching a real estate career-no college degree required.
References
- [1] Tennessee Real Estate Commission (2025). How to Get a License.
- [2] Kaplan Real Estate Education (2024). How to Become a Real Estate Agent.
- [3] Colibri Real Estate (2025). Massachusetts Real Estate Agent License Requirements.
- [4] National Association of REALTORS® (2012). Real Estate Designations and Certifications.
- [5] Virginia Department of Professional and Occupational Regulation (2004). Real Estate Board.
MORE FROM couponito.com